'정보 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python 손글씨 검출 GUI (0) | 2024.09.27 |
|---|---|
| Python PyQt (4) | 2024.09.27 |
| Python 손글씨 검출 (6) | 2024.09.27 |
| python YOLOv5 사용방법 (2) | 2024.09.27 |
| python 기초2 (0) | 2023.01.10 |




| Python 손글씨 검출 GUI (0) | 2024.09.27 |
|---|---|
| Python PyQt (4) | 2024.09.27 |
| Python 손글씨 검출 (6) | 2024.09.27 |
| python YOLOv5 사용방법 (2) | 2024.09.27 |
| python 기초2 (0) | 2023.01.10 |
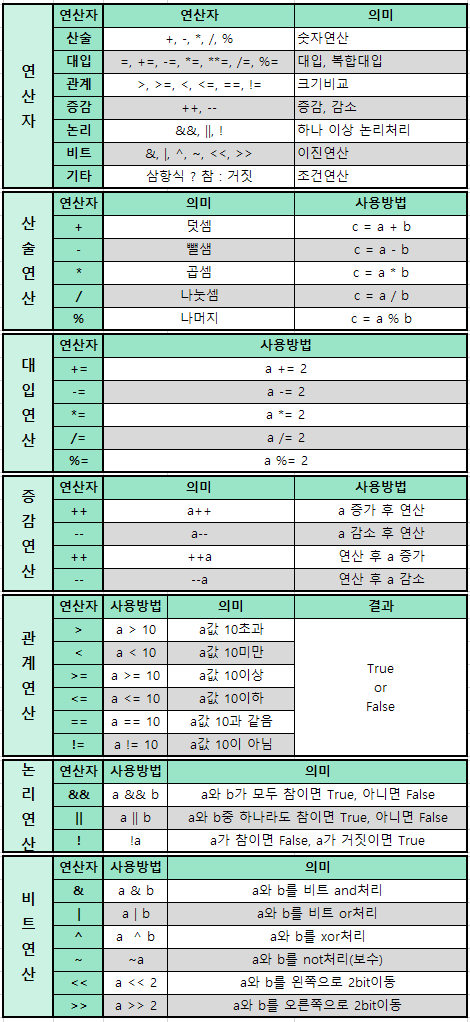
int a = 10; // a변수에 10 저장
int b = 20; // b변수에 20 저장
int c = 30; // c변수에 30 저장
System.out.println(a<b); // a가 b보다 작아? true
System.out.println(a>b); // a가 b보다 커? false
System.out.println(a+b<=c); // a+b가 c보다 작거나 같아? true
System.out.println(a+b>=c); // a+b가 c보다 크거나 같아? true
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
boolean a = true; // a 변수에 true 값 저장
boolean b = false; // b 변수에 false 값 저장
boolean c = !a; // c 변수에 a가 true 라면 false, false 라면 true값 저장
System.out.println(a); //true
System.out.println(!a); //false
System.out.println(b); //false
System.out.println(c); //false
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int a = 1; // a 변수에 1값 저장
System.out.println(a);
a++; // a값 1증가: 후위형
System.out.println(a); // 이 떄, a는2
System.out.println(++a); // a의 값 1증가, 전위형: 증가가 먼저 출력:3
System.out.println(a++); // a의 값 1증가, 후위형: 증가가 나중에 출력:3
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int a = 10; //a 변수에 10값 저장
int b = 3; // b변수에 3값 저장
double doubleB = 3; //자동형변환
System.out.println(a+b);
System.out.println(a-b);
System.out.println(a*b);
System.out.println(a/b);
System.out.println(a%b);
System.out.println(a/doubleB); // 정수 / 실수 = 실수
System.out.println(a%doubleB); // 정수 % 실수 = 실수
System.out.println(doubleB%b); // 실수 % 정수 = 실수
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int a = -1; // a 변수에 -1 저장
int b = 2; // b변수에 2를 저장
System.out.println(a); // -1
System.out.println(-b); // -2
| equals (문자열 비교하기) (0) | 2023.01.08 |
|---|---|
| 변수 (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 데이터 타입과 형변환 (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 스캔(값 입력받기) (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 프린트 및 문자형태 (0) | 2022.12.14 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 3.14; // 실수형 변수 a에 3.14저장
double b = 5.15; // 실수형 변수 b에 5.15저장
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a!=b);
String c1 = "hello JAVA!"; //c1 문자열 변수에 "hello JAVA!" 값 저장
System.out.println(c1 == "hello JAVA!"); // true
System.out.println(c1.equals("hello JAVA!")); // true (문자열 비교할 떄는 equals사용)
// 문자열.equals(비교 문자열) : 문자열 비교하기
System.out.println(c1.equals("hello java!")); // 대/소문자 까지 비교
| 연산자 (0) | 2023.01.08 |
|---|---|
| 변수 (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 데이터 타입과 형변환 (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 스캔(값 입력받기) (0) | 2022.12.15 |
| 프린트 및 문자형태 (0) | 2022.12.14 |
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<textarea name="txt" id="txt" cols="30" rows="20"></textarea><br/>
<label for="text-color">글자색 변경</label>
<input type="color" id="text-color" value="#FFF"><br />
<label for="bg-color">배경색 변경</label>
<input type="color" id="bg-color" value="#FFF"><br />
<button id="set-color">설정 저장하기</button>
<button id="get-color">설정 불러오기</button>
<button id="clear">설정 초기화</button>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const textArea = document.getElementById('txt');
const textColor = document.getElementById('text-color');
const bgColor = document.getElementById('bg-color');
const setBtn = document.getElementById('set-color');
const getBtn = document.getElementById('get-color');
const clearBtn = document.getElementById('clear');
// 글자색 변경 부분이 색이 ㅂ녀경되었다면
textColor.onchange = () => {
// 텍스트 에리아의 색을 변경
textArea.style.color = textColor.value;
};
// 배경색 변경 부분의 색이 변경되었다면
bgColor.onchange = () => {
// 텍스트 에리어의 배경을 변경
textArea.style.backgroundColor = bgColor.value;
};
setBtn.onclick= () => {
// color 값들을 모두 받아서 객체 형태로 저장함
const colorObj = {txtColor:textColor.value, bgColor:bgColor.value};
const jsonObj = JSON.stringify(colorObj);
console.log(jsonObj);
// 로컬스토리지에 현재 textColor의 값을 'txtColor' key 이름으로 저장함
localStorage.setItem("textAreaColor", jsonObj);
alert('설정을 저장했습니다!');
}
getBtn.onclick= () => {
alert('설정을 불러왔습니다!');
const textAreaColor = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('textAreaColor'));
// 텍스트 에리어 값을 변경
textArea.style.color = textAreaColor.txtColor;
textArea.style.backgroundColor = textAreaColor.bgColor;
// 색상 input값을 변경
textColor.value = textAreaColor.txtColor;
bgColor.value = textAreaColor.bgColor;
}
clearBtn.onclick= () => {
let length = localStorage.length;
while(length > 0){
localStorage.removeItem(localStorage.key(0));
length--;
}
alert('설정 정보를 삭제하였습니다.');
}
</script>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
// promise : 비동기 처리를 위해 ES6부터 지원되는 비동기 함수
// promise 생성자 함수는 비동기 처리를 수행할 콜백 함수(executor 함수)를 인수로 전달받음
// executor는 resolve, reject라는 두 개의 함수르 인수로 전달받음
// promise는 생성되는 순간 바로 executor 를 실행함(중요!)
// promise는 실행이 끝난 promise 객체를 반환함
// Promis 상태 -
// 1) prnding : 비동기 처리가 아직 수행되징 않은 상태로, 프로미스 생성 직후 상태
// 2) fulfiled : 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태(성공)로, resolve가 호출된 상태
// 3) rejected : 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태(실패)로 , reject가 호출도니 상태
// 생성자. producer - promise를 생성하는 쪽
// const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{
// if(true){// 비동기 처리가 성공했을 시
// resolve('result');
// }
// else {// 비동기 처리 실패 시
// reject('failure reason')
// }
// });
// Consumer 소비자, Promise 객체(의 내부 함수)를 소비하는 쪽
// Promise의 후속처리 메서드
// 1) then
// - 두 개의 콜백 함수를 인수로 전달받음
// - Promise가 fulfiled된 상태 (resolve 호출) Promise의 처리 결과를 인수로 받음
// - Promise가 rejected된 상태 (reject 호출) Promise 의 에러를 인수로 받음
// const successedPromise = new Promise ((resolve, reject)=>{
// resolve('성공했다');
// });
// const faliededPromise = new Promise ((resolve, reject)=>{
// reject('실패했다');
// });
// faliededPromise.then(
// value => { console.log('val: ', value);},
// e => { console.log('e: ', e);}
// );
// // 2) catch
// // - 한 개의 콜백 함수를 인수로 전달받음
// // - Promise가 rejected 된 상태의 경우만 호출되며, Promise의 에러를 인수로 받음
// // - then과 동일하게 동작함
// //
// new Promise((res, rej)=> rej(new Error('실패되었음')))
// .catch((e)=> { console.log(e);
// });
// // 3) finally
// // - 한 개의 콜백 함수를 인수로 전달받음
// // - Promise성공 실패 상관없이 호출됨
// new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// // resolve('성공입니다.!');
// reject('실패입니다.!');
// }).finally(() => {
// console.log('마지막입니다.');
// });
// // Promise를 사용한 예외처리
// let errorPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{
// setTimeout(()=>{
// try{
// throw new Error('에러났다!!!!!!!!');
// resolve();
// }catch(e){
// reject(e);
// }
// },3000)
// });
// errorPromise.then(
// value => {},
// error => {
// console.log('에러가 나버렸다');
// console.log('에러: ', error)
// }
// );
// let testPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{
// setTimeout(()=>{resolve(f1)},1000)
// });
// testPromise.then(
// value => {value()},
// error => {}
// ).then(
// value => {f2()},
// error => {}
// ).then(
// vlaue => {f3()},
// error => {}
// )
// function f1(){
// console.log('f1이 실행되었음');
// }
// function f2(){
// console.log('f2이 실행되었음');
// }
// function f3(){
// console.log('f3이 실행되었음');
// }
const data1 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(()=> resolve(3),3000))
const data2 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(()=> resolve(2),2000))
const data3 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(()=> resolve(1),1000))
// const data1 = () => new Promise((_, rej) => setTimeout(()=> rej(3),3000))
// const data2 = () => new Promise((_, rej) => setTimeout(()=> rej(2),2000))
// const data3 = () => new Promise((_, rej) => setTimeout(()=> rej(1),1000))
Promise.all([data1(), data2(), data3()]) // 마지막 처리가 끝나면 동시에 출력
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log);
Promise.race([data1(), data2(), data3()]) // 제일 빨리 처리한것만 출력
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log);
setTimeout(() => console.log('10'),0);
Promise.resolve()
.then(()=> console.log(20))
.then(()=> console.log(30));
const promises = [];
data1().then( value => {
promises.push(value);
return data2()
})
.then(value => {
promises.push(value);
return data3()
})
.then(value => {
promises.push(value);
console.log(promises)
})
</script>| js 시계 + 타이머 만들기 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
|---|---|
| setTimeout / setInterval 사용 요약 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용2 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용1 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| js 기초6 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log('첫번째 함수 끝');
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log('두번째 함수 끝');
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log('세번째 함수 끝');
},3000);
},2000);
},1000);
console.log('1');
setTimeout(() => { console.log('2')},1000);
console.log('3');
console.log('최종 delay:', print_delay(print, 2000));
print_immediateely(print);
function print_immediateely(func){
func('immediately');
}
function print_delay(func, time){
let delay = 'delay';
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log('변하기 전 delay:', delay)
delay = 30000;
console.log('변한 후 delay:', delay)
}, time);
return delay;
}
function print(massage) {
console.log(massage, '함수실행');
}
try{
setTimeout(()=>{
throw new Error('에러났당');
},3000);
//set
}catch(e){
console.log(e)
console.log('에러났네..')
}
</script>
HTML코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>전자시계</title>
<script src="2_Clock.js" defer></script>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<div id="click-container">
<div id="date-now"><i>현재날짜: </i><span></span></div>
<div id="time-now"><i>현재시간: </i><span></span></div>
</div>
<div id="timer-container">
<div>
<div id="timer"><span>00:00:00</span></div>
<button>시작/재시작</button>
<button>일시정지</button>
<button>초기화</button>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>js 코드
const dateNow = document.querySelector('#date-now > span'); //현재 날짜 부분
const timeNow = document.querySelector('#time-now > span'); //현재 시간 부분
const timer = document.querySelector('#timer > span'); //타이머 시간 부분
const btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button'); //모든 버튼
const startBtn = btns[0]; //시작버튼
const stopBtn = btns[1]; //중지버튼
const clearBtn = btns[2]; //초기화버튼
const timerStatus = { RUNNING: true, STOP: false }; //enum처럼 상태 객체를 만들기
let nowStatus = timerStatus.STOP; //타이머의 상태를 저장하는 변수 (기본값: STOP)
let timerID = ""; // 1초마다 타이머를 갱신시킴
//0.2초마다 날짜를 갱신
setInterval(date_setting, 200);
// Start 버튼을 눌렀다면
startBtn.onclick = () => {
//타이머 id를 받아오고, 1초마다 타이머가 시작하도록 함
nowStatus = timerStatus.RUNNING;
if(timerID === ""){
timerID = setInterval(timer_setting, 100);
}
}
stopBtn.onclick = () => {
if(timerID !== ""){
nowStatus = timerStatus.STOP;
}
}
clearBtn.onclick = () => {
//timerID가 존재하면(빈문자열이아니면) interval을 중지하고, 그게 아니면 timerID를 그대로(빈문자열로) 둔다
if(timerID !== ""){
clearInterval(timerID);
timerID = ""; //timerID를 초기화한다
timer.textContent = "00:00:00"; //문자열을 처음으로 돌린다
}
}
//현재 날짜 정보를 설정하는 함수
function date_setting(){
//날짜를 설정하기 위한 Date객체를 생성한다
const date = new Date();
//날짜 문자열을 생성
const dateString = `${date.getFullYear()}-${format_setting(date.getMonth() + 1)}-${format_setting(date.getDate())}`;
//현재 날짜 부분을 실제 날짜로 변경
dateNow.textContent = dateString;
//시간 문자열을 생성
const timeString = `${format_setting(date.getHours())}:${format_setting(date.getMinutes())}:${format_setting(date.getSeconds())}`;
timeNow.textContent = timeString;
}
//status: 현재 동작중인지, 정지상태인지 설정하는 상태 변수
function timer_setting(){
if(nowStatus === timerStatus.STOP){ return; }
let timerNowString = timer.textContent; //현재 진행된 타이머 시간
let times = timerNowString.split(':'); // ':'으로 문자열을 나눈다
let hour = +times[0]; //시
let min = +times[1]; //분
let sec = +times[2]; //초
sec++; //1초 증가시킴
if(sec >= 60){ //1초 증가했는데 60초가 되었다?
min++; //1분 증가시킴
sec = 0; //초를 0으로 돌림
}
if(min >= 60){ //1분 증가했는데 60분이 되었다?
hour++; //1시간 증가시킴
min = 0; //분을 0으로 돌림
}
if(hour >= 24){ //1시간 증가했는데 24시간이 되었다?
hour = 0; //hour를 0으로 돌림
clearInterval(timerID); //타이머를 중지시킴
}
//1초가 지난 현재 타이머 시간을 문자열로 생성
const timerSting = `${format_setting(hour)}:${format_setting(min)}:${format_setting(sec)}`;
//타이머 시간 표시 부분에 문자열을 설정
timer.textContent = timerSting;
}
//날짜나 시간 형식을 00:00:00 형태로 만들어주기 위한 포맷 형식
function format_setting(data){ //data -> 월, 일, 시, 분, 초 중에 하나가 들어옴 (string)
// data 를 문자열로 바꿧을 때 한 글자면 앞에 0을 붙여서 반환시킨다.
return data.toString().length < 2 ? '0' + data : data;
}
| promise (0) | 2023.01.03 |
|---|---|
| setTimeout / setInterval 사용 요약 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용2 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용1 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| js 기초6 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
// JS는 기본 싱클 스레드로 동작함(single thread)
// 따라서, JS는 두 가지 이상의 일(task)를 동시 실행할 수 없음.
// 타이머 함수 (setTimeout, setInterval) -> JS가 처리하는게 아니라, web 에서 처리함. 따라서 병렬로 작업함
// setTimeout: 일정시간 후에 한번 전달받은 함수를 실행함(한번동작)
// setInterval: 일정시간마다 전달받은 함수를 실행(반복동작)
// - handler : 내가 실행하고 싶은 함수
// - timeout : 일정 시간 이후 실행할 초(ms, 1/1000)
// - 값을 지정하지 않을 시, 기본값 0이 지정됨 최소4ms지난 후 실행됨.
// - ...arguments : 실행하고 싶은 함수에 전달할 인자들을 순서대록 작성
//
const id = setTimeout(print, 1000, '실행했어', 300);
clearTimeout(id);//작업 설정한 id를 전달하여 예약된 작업을 취소
setTimeout(() =>{
console.log('함수가실행됬다')
},2000);
function print(message, number){
console.log(message)
console.log(number)
}
const intwervalId = setInterval(print2, 500);
setTimeout(()=>{
clearInterval(intwervalId)
}, 1500);
function print2(){
console.log('반복작업1');
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>| promise (0) | 2023.01.03 |
|---|---|
| js 시계 + 타이머 만들기 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용2 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| addEventListener 활용1 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| js 기초6 (0) | 2023.01.03 |